What is a Health and Safety Audit?
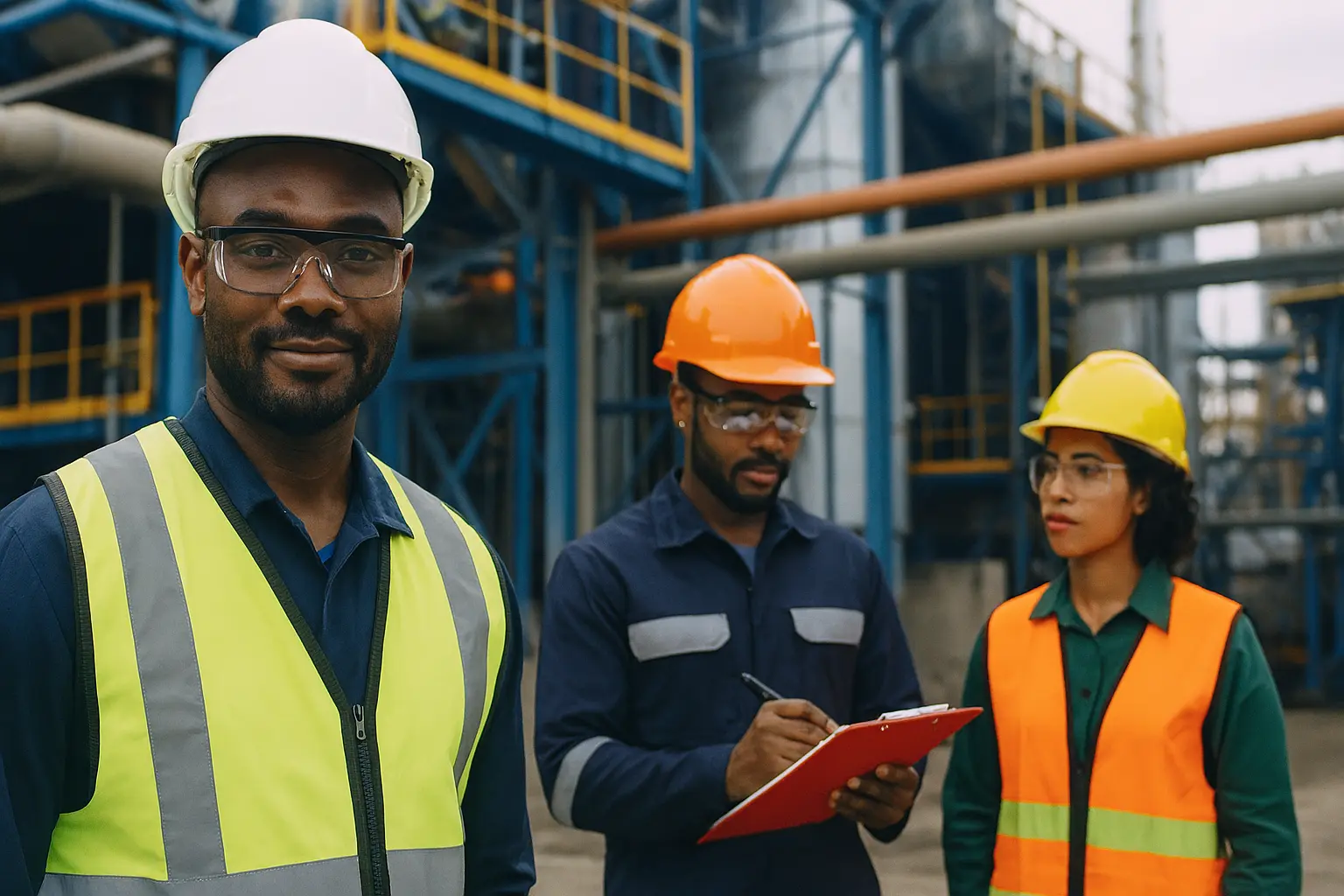
Every occupier is required to cause a health and safety audit of the workplace at least once in every period of 12 months by a health and safety adviser registered for that purpose by the Director of Occupational health and safety as per Section 10 of Legal Notice No 31 of 2004.The main legislation which is relevant to this subject is the Occupational Safety and Health Act, 2007 and its subsidiary legislations. A Health and Safety Audit of workplaces and their associated operations is a way of periodically checking if and how they are complying with requirements of the Occupational Safety and Health Act, 2007. It also allows comparisons to be made between the areas that are performing well regarding health and safety management and those that are not. The health and safety audit is carried out as per the code of practice for health and safety auditing. This is done by a DOSHS approved health and safety auditor. The outcome of the audit is documented and a copy of the report submitted to the Directorate of Occupational Health and Safety Services as required under Sec. 13 (1) of Legal Notice No. 31 under the Occupational Safety and Health Act, 2007 of the laws of Kenya. Our team will also offer advice and guidance on actions necessary to enable the company to fully comply with health & safety regulations and best industry practice. We also walk with you towards ensuring that the company fully complies with all the requirements of the OSHA 2007 and all its subsidiary legislation as well as ensuring the company achieves a reasonable level of safety culture.
"A Health and Safety Audit is more than a statutory requirement, it is a proactive step toward protecting your workforce, safeguarding your assets, and building a culture of safety."
TERMS OF REFERENCE OF THE SAFETY AND HEALTH AUDIT
The audit will be carried out with the main objective of evaluating compliance of the workplace and its operations with the provisions of the Occupational Safety and Health Act, 2007 and all the relevant subsidiary legislations. The audit as well is intended to establish EHS provisions and management gaps with the view of providing recommendations for the purpose of improvement where applicable.
AUDIT OBJECTIVES
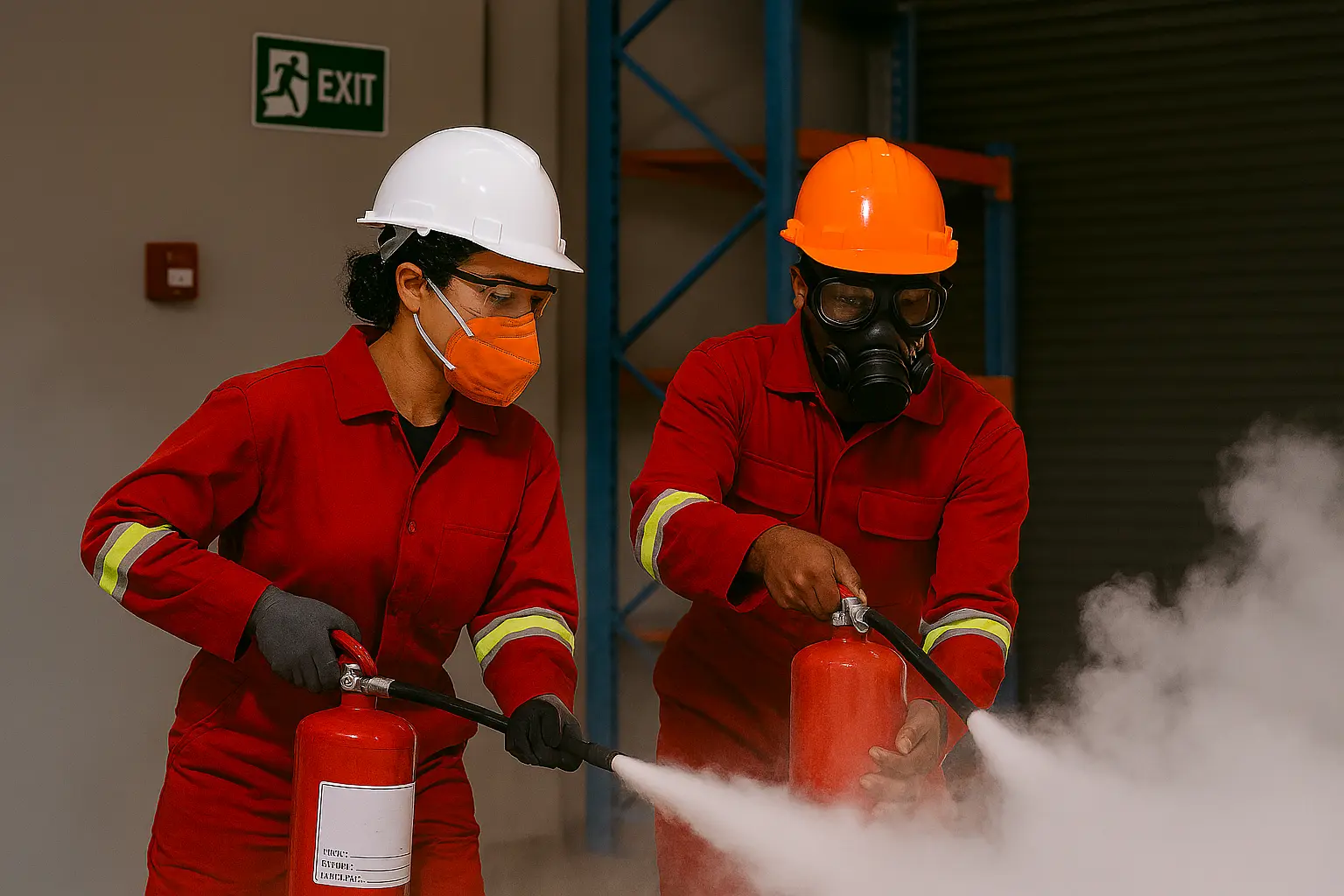
The Auditors main objective will be to assess occupational health and safety issues that are as a result of the workplace operations of the effectiveness of the mitigation measures currently in place for ensuring occupational health and safety of the personnel, installations and surrounding environment.
- Assess the status of the facilities in line with the requirements defined in the Occupational Health and Safety of 2007, document the findings in the acceptable audit report and report this to the DOSHS by submitting a detailed report of the findings and recommendations made.
- Review and evaluation of other recommendations made by either health and safety advisers or officers who may have visited this workplace in the past twelve months.
- Review and evaluation of the progress made in the Implementation of the recommendations made in the previous Health and Safety audit reports.
- Advice and give recommendations to the Occupier, employees and other stakeholders on matters relating to occupational Health and Safety in this workplace.
- Employee occupational health and safety awareness levels and The Workplace’s compliance to all Legal Notices regulated by OSHA2007
- Prepare the workplace statutory Occupational Health and Safety audit annual report in fulfilment of the legal requirement in accordance with OSHA 2007.
AUDIT METHODOLOGY
The audit methodology shall comprise six fundamental steps:

- Pre-audit/preliminary or opening meetings
- Desk review of available health and safety documents
- Sites inspection and data gathering through questionnaires and interviews
- Data analysis (comparing findings to expectations in the cited legal frameworks)
- Post-audit/feedback or closing meetings and presentation of draft health and safety reports Presentation of final health and safety reports to both management and the DOSHS